C语言代码集
title: 代码集
date: 2020-03-29 19:35:14
tags:
- 竞赛
categories: 技术
简介
博主我隔离期间实在无聊于是无聊到整理代码模版
从入门到放弃
基础
输入类
读入优化
1 | |
高精度
高精度真的是mol鬼,到现在听到要打高精度觉得自己还是打不出来
1 | |
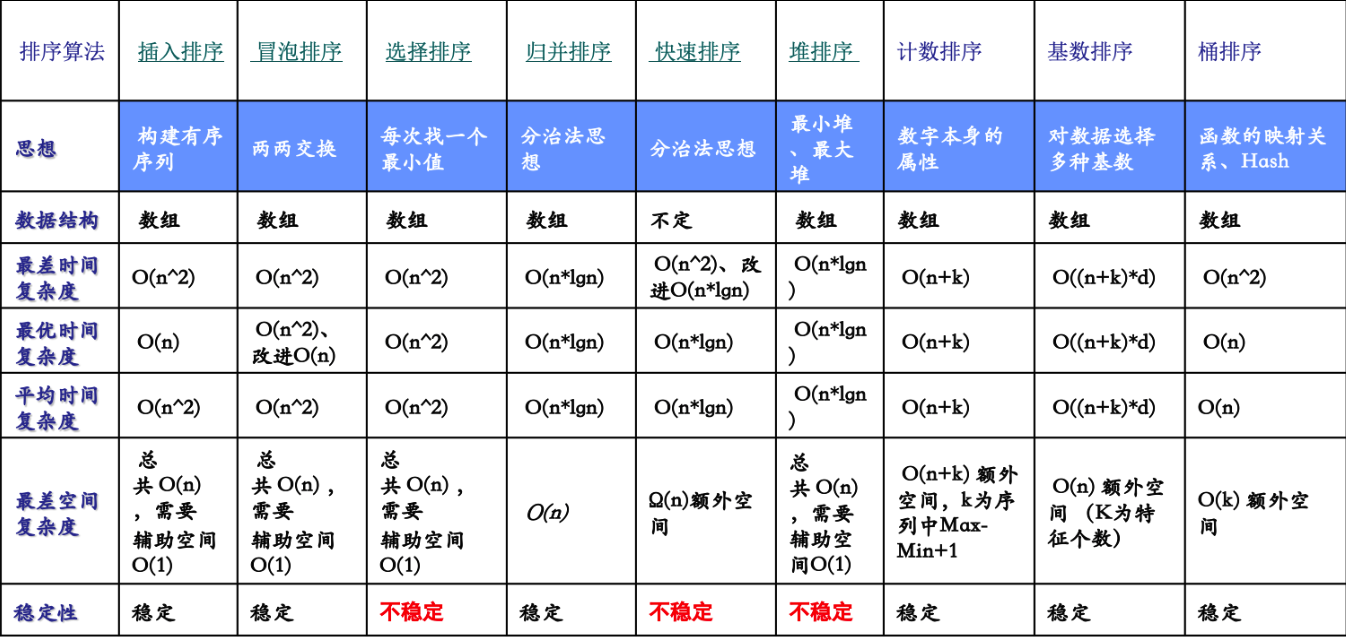
排序
真香排序
不论会什么高级模版,总会想用它
1 | |
桶排
简单来说就是记录后找下标
1 | |
冒泡排序
相邻元素若不按照顺序则替换
1 | |
归并排序
递归拆分子序列
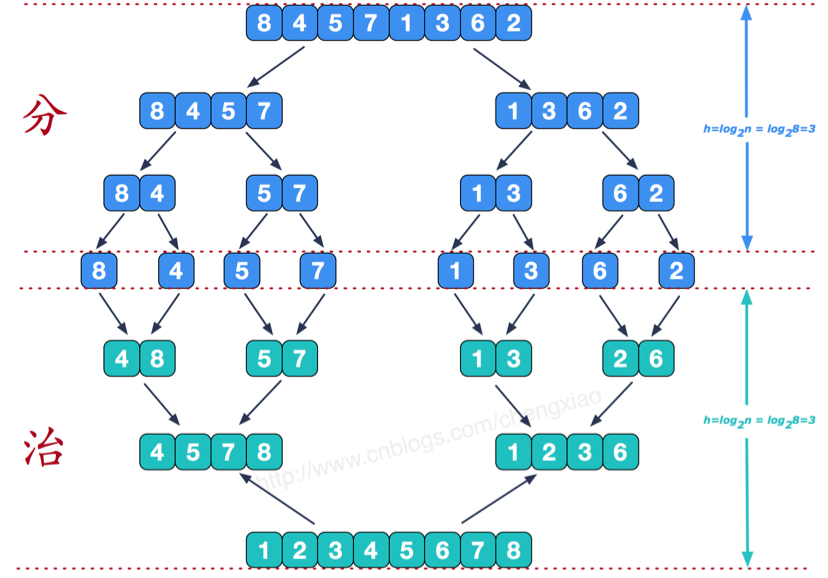
1 | |
快速排序
基本思想是通过一趟排序将待排记录分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分记录的均比另一部分小,则可分别对这两部分记录继续进行排序,以达到整个序列有序.
假定待排序列为{r[s],r[s+1],…..r[t]},首先选取一个记录作为枢轴(pivot),然后按下述原则重新排列其余记录.
将所有较它小的记录安置在它之前,将所有较它大的记录安置在它之后.由此可见此”枢轴”记录最后所落的位置I作分界线,将原序列分割成两个{r[s],r[s+1],…r[i-1]}和{r[i],r[i+1],…r[t]}.这个过程称做一趟快速排序(或一次划分).
1 | |
进制转换
1 | |
提高
图论
默认存储及加边
1 | |
DFS
1 | |
BFS
1 | |
Dijkstra
1 | |
Floyd
1 | |
SPFA
1 | |
Difference between Dij+heap and SPFA!!!
Dij:
1 | |
SPFA:
1 | |
So the difference is clear enough:
Dji+heap: Small root pile, every time get the shortest distance, for this point, the shortest distance won’t change!
SPFA: Use queue. Get the front out of queue, might be renew in the future, it is won’t be always the same.
复杂度
Usage
| Shortest-PathsProblem | Sparse Graph | Dense Graph | With negative value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Source | Dijkstra+heap | SPFA/Dijkstra+heap | SPFA |
| APSP(Undirected graph) | SPFA/Floyd | SPFA | SPFA |
| APSP(Directed graph) | Floyd | SPFA/Dijkstra+heap | SPFA |
APSP((All Pairs Shortest Path))
Complexity
| Solving ways | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Dijkstra+heap | O(E*lgV) | O(n^2) |
| SPFA | O(kE) (Not stable) | O(n) |
| Floyd | O(n^3) | O(n) |
树论
线段树
1 | |
树状数组
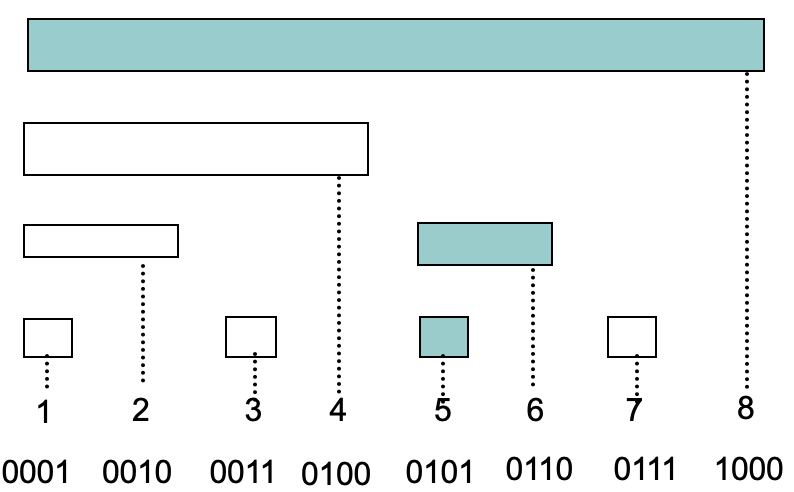
1 | |
重链剖分+lca
1 | |
离散化
离散化后只能知道数据之间的相对大小,但无法确定它们的真实值;
离散化的三个步骤:
1 sort排序
2 unique去重
3 lower_bound索引
1 | |
并查集
1 | |